Elbow
Elbow Anatomy
The elbow is a complex joint formed by the articulation of three bones – the humerus, radius and ulna. The elbow joint helps in bending or straightening of the arm to 180 degrees and assists in lifting or moving objects.
The bones of the elbow are supported by:
- Ligaments and tendons
- Muscles
- Nerves
- Blood vessels
Bones & Joints of the elbow joint
The elbow joint is formed at the junction of three bones:
- The Humerus (upper arm bone) forms the upper portion of the joint. The lower end of the humerus divides in to two bony protrusions known as the medial and lateral epicondyles which can be felt on either side of the elbow joint.
- The Ulna is the larger bone of the forearm located on the inner surface of the joint. The curved shape of the ulna articulates with the humerus.
- The Radius is the smaller bone of the forearm situated on the outer surface of the joint. The head of the radius is circular and hollow which allows movement with the humerus. The connection between the ulna and radius helps the forearm to rotate.
The elbow consists of three joints because of articulation of the three bones namely:
- Humero-ulnar joint is formed between the humerus and ulna and allows flexion and extension of the arm.
- Humero-radial joint is formed between the radius and humerus, and allows movements like flexion, extension, supination and pronation.
- Radio-ulnar joint is formed between the ulna and radius bones, and allows rotation of the lower arm.
Articular cartilage lines the articulating regions of the humerus, radius and ulna. It is a thin, tough, flexible, and slippery surface that acts as a shock absorber and cushion to reduce friction between the bones. The cartilage is lubricated by synovial fluid, which further enables the smooth movement of the bones.
Muscles of the elbow joint
There are several muscles extending across the elbow joint that help in various movements. These include the following:
- Biceps brachii: upper arm muscle enabling flexion of the arm
- Triceps brachii: muscle in the back of the upper arm that extends the arm and fixes the elbow during fine movements
- Brachialis: upper arm muscle beneath the biceps which flexes the elbow towards the body
- Brachioradialis: forearm muscle that flexes, straightens and pulls the arm at the elbow
- Pronator teres: this muscle extends from the humeral head, across the elbow, and towards the ulna, and helps to turn the palm facing backward
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis: forearm muscle that helps in movement of the hand
- Extensor digitorum: forearm muscle that helps in movement of the fingers
Elbow joint ligaments and tendons
The elbow joint is supported by ligaments and tendons, which provide stability to the joint.
Ligaments are a group of firm tissues that connect bones to other bones. The most important ligaments of the elbow joint are the:
- Medial or ulnar collateral ligament: comprised of triangular bands of tissue on the inner side of the elbow joint.
- Lateral or radial collateral ligament: a thin band of tissue on the outer side of the elbow joint.
Together, the medial and lateral ligaments are the main source of stability and hold the humerus and ulna tightly in place during movement of the arm.
- Annular ligament: It is a group of fibers that surrounds the radial head, and holds the ulna and radius tightly in place during movement of the arm.
The ligaments around a joint combine to form a joint capsule that contains synovial fluid.
Any injury to these ligaments can lead to instability of the elbow joint.
Tendons are bands of connective tissue fibers that connect muscle to bone. The various tendons which surround the elbow joint include:
- Biceps tendon: attaches the biceps muscle to the radius, allowing the elbow to bend
- Triceps tendon: attaches the triceps muscle to the ulna, allowing the elbow to straighten
Nerves of the elbow joint
The main nerves of the elbow joint are the ulnar, radial and median nerves. These nerves transfer signals from the brain to the muscles that aid in elbow movements. They also carry the sensory signals like touch, pain, and temperature back to the brain.
Any injury or damage to these nerves causes pain, weakness or joint instability.
Blood vessels
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-pure blood from the heart to the hand. The main artery of the elbow is the brachial artery that travels across the inside of the elbow and divides into two small branches below the elbow to form the ulnar and the radial artery.
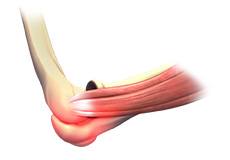
Elbow Sprain
Elbow sprain is an injury to the soft tissues of the elbow. It is caused due to stretching or tearing (partial or full) of the ligaments which support the elbow joint. Ligaments are a group of fibrous tissues that connect one bone to another in the body.
The Elbow is a complex hinge joint formed by the articulation of three bones - humerus, radius and ulna. .
Elbow Fractures
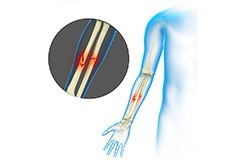
Adult Forearm Fractures
The forearm is made up of 2 bones, namely, the radius and ulna. The primary function of your forearm is rotation i.e., the ability to turn your palm up and down. The fracture of the forearm affects the ability to rotate your arm, as well as bend and straighten the wrist and elbow. The breaking of the radius or ulna in the middle of the bone requires a strong force and it is most commonly seen in adults. In most of the cases, both bones are broken during a forearm fracture.
Forearm Fractures in Children
The radius (bone on the thumb side) and ulna (bone on the little-finger side) are the two bones of the forearm. Forearm fractures can occur near the wrist, near the elbow or in the middle of the forearm. Apart from this, the bones in children are prone to a unique injury known as a growth plate fracture. The growth plate, which is made of cartilage (flexible tissue) is present at the ends of the bones in children and helps in the determination of length and shape of the mature bone.
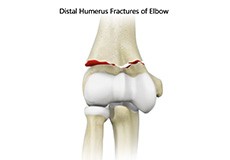
Distal Humerus Fractures of the Elbow
The elbow is a region between the upper arm and the fore arm. The elbow joint is made up of 3 bones. The distal (lower) end of the humerus bone in the upper arm joins with the radius and ulna bones in the fore arm to form the elbow joint. The elbow joint is very important for the movement of your arms and for coordination of daily activities. Injury in the distal humerus can cause impairment in the function of the elbow joint.

Elbow Fractures in Children
The elbow is a joint that consists of three bones – the humerus (upper arm bone), radius (forearm bone) and ulna (forearm bone). An elbow fracture most commonly occurs when your child falls on an outstretched arm. It can lead to severe pain in the elbow and numbness in the hand. Fractures are more common in children due to their physical activities as well as their bone properties.
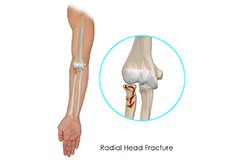
Radial Head Fractures of the Elbow
The elbow is a junction between the forearm and the upper arm. The elbow joint is made up of 3 bones, namely the humerus bone in the upper arm which joins with the radius and ulna bones in the forearm. The elbow joint is essential for the movement of your arms and to perform daily activities. The head of the radius bone is cup-shaped and corresponds to the spherical surface of the humerus.
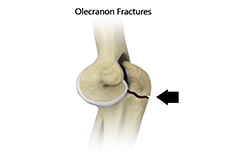
Elbow Fractures
Three bones, the humerus, radius and ulna, make up the elbow joint. Elbow fractures may occur from trauma, resulting from various reasons; a fall on an outstretched arm, a direct blow to the elbow, or an abnormal twist to the joint beyond its functional limit.
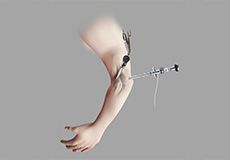
Elbow Arthroscopy
Elbow arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, is performed through tiny incisions to evaluate and treat several elbow conditions.
The Elbow is a complex hinge joint formed by the articulation of three bones - humerus, radius and ulna.











